Module 3.1 - Efficiency¶
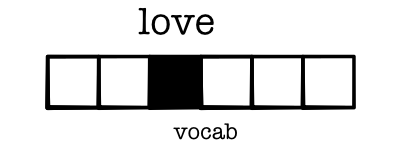
What is a word?¶
- Treat words as index in vocabulary
- Represent as a one-hot vector
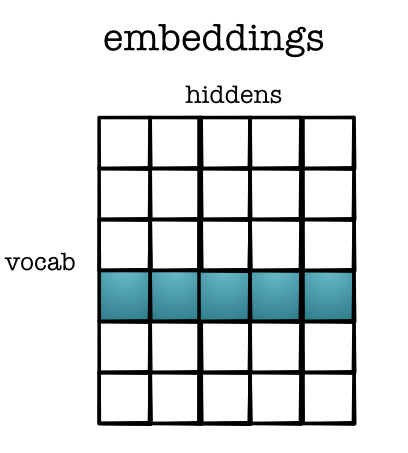
Layer 1¶
- First layers is called an
embedding
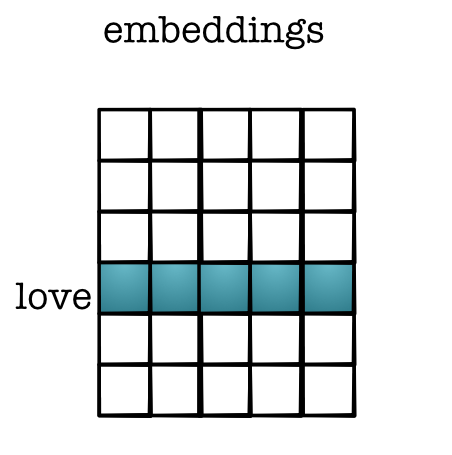
Hidden vector for word¶
Get word vector
word_one_hot = tensor([0 if i != word else 1
for i in range(VOCAB)])
embedding = (layer1 * word_one_hot).sum(1)
How does this share information?¶
- Similar words have similar embedding dim
- Dot-product - easy way to tell similarity
(word_emb1 * word_emb2).sum()- Differentiable!
Where do these come from?¶
- Trained from a different model
- Extracted and posted to use
- (Many more details in NLP class)
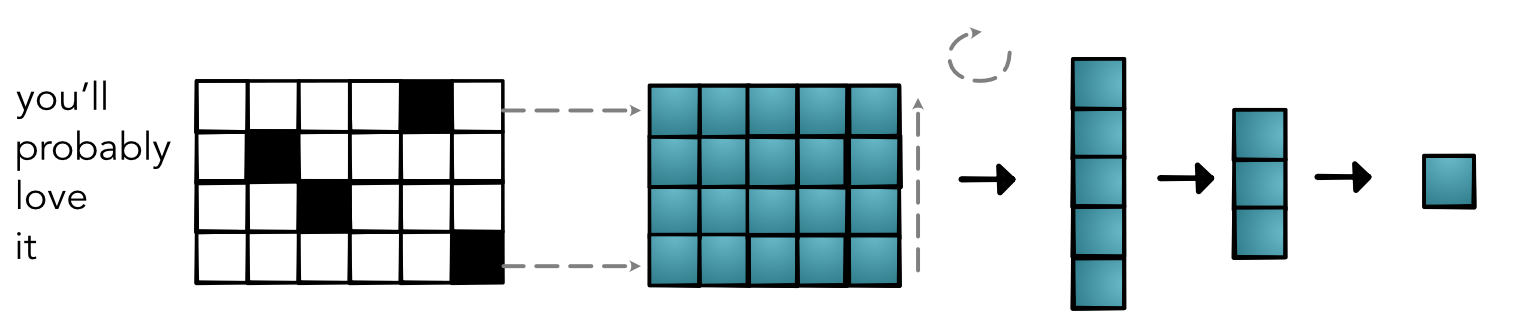
Full Model¶
Quiz¶
Cult of Efficiency¶
Context¶
- We now have a pytorch
- All wrappers around
ops - Need to make
opsfast
Code¶
Example map
for i in range(len(out)):
count(i, out_shape, out_index)
broadcast_index(out_index, out_shape, in_shape, in_index)
o = index_to_position(out_index, out_strides)
j = index_to_position(in_index, in_strides)
out[o] = fn(in_storage[j])
Why are Python (and friends) "slow"?¶
- Function calls
- Types
- Loops
Function Calls¶
- Function calls are not free
- Checks for args, special keywords andm lists
- Methods check for overrides and class inheritance
Types¶
Critical code
out[o] = in_storage[j] + 3
- Doesn't know type of
in_storage[j] - May need to coerce 3 to float or raise error
- May even call
__add__or__ladd__!
Loops¶
- Loops are always run as is.
- Can't combine similar loops or pull out constant computation.
- Very hard to run anything in parallel.
Notebook¶
Fast Math¶
How does it work?¶
Work
def my_code(x, y):
for i in range(100):
x[i] = y + 20
...
my_code(x, y)
fast_my_code = numba.njit()(my_code)
fast_my_code(x, y)
fast_my_code(x, y)
Notebook¶
Terminology : JIT Compiler¶
- Just-in-time
- Waits until you call a function to compile it
- Specializes code based on the argument types given.
Terminology : LLVM¶
- Underlying compiler framework to generate code
- Used by many different languages (C++, Swift, Rust, ...)
- Generates efficient machine code for the system
What do we lose?¶
njitwill fail for many python operations- No lists, classes, python functions allowed
- Any different types will cause recompilation
Strategy¶
- Use Python for general operations
- Use Numba for the core tensor ops
- Allow users to add new Numba functions
Code Transformation¶
Transform
def my_code(x, y):
for i in prange(100):
x[i] = y + 20
...
my_code(x, y)
fast_my_code = numba.njit(parallel=True)(my_code)
fast_my_code(x, y)
fast_my_code(x, y)
Parallel¶
Parallel¶
- Run code on multiple threads
- Particularly suited for map / zip
- Baby steps towards GPU
Parallel Range¶
- Replace
forloops with parallel version - Tells compiler it can run in any order
- Be careful! Ideally these loops don't change anything
Code Transformation¶
Transform ::
def my_code(x, y):
for i in prange(100):
x[i] = y + 20
...
my_code(x, y)
fast_my_code = numba.njit(parallel=True)(my_code)
fast_my_code(x, y)
fast_my_code(x, y)
Nondeterminism¶
- No guarantee on ordering
- Need to be careful with reductions
- Speedups will depend on system
Parallel Bugs¶
- Warning! Nasty bugs
- Tests failing randomly
- Crashes due to out-of-bounds
Parallel Diagnostics¶
- Diagnostics give parallel compilation
- Useful to see if you are getting benefits

