Module 4.0 - Networks¶
Fusion¶
- Optimization across operator boundary
- Save speed or memory in by avoiding extra forward/backward
- Can open even great optimization gains
Simple Matmul Pseudocode¶
for outer_index in out.indices():
for inner_val in range(J):
out[outer_index] += A[outer_index[0], inner_val] * \
B[inner_val, outer_index[1]]
Compare to zip / reduce¶
Code
ZIP STEP
C = zeros(broadcast_shape(A.view(I, J, 1), B.view(1, J, K)))
for C_outer in C.indices():
C[C_out] = A[outer_index[0], inner_val] * \
B[inner_val, outer_index[1]]
REDUCE STEP
for outer_index in out.indices():
for inner_val in range(J):
out[outer_index] = C[outer_index[0], inner_val,
outer_index[1]]
Basic CUDA - Square Large¶
Basic CUDA ::
In [2]:
def mm_shared1(out, a, b, K):
...
for s in range(0, K, TPB):
sharedA[local_i, local_j] = a[i, s + local_j]
sharedB[local_i, local_j] = b[s + local_i, j]
...
for k in range(TPB):
t += sharedA[local_i, k] * sharedB[k, local_j]
out[i, j] = t
Non-Square - Dependencies¶
Challenges¶
How do you handle the different size of the matrix?
How does this interact with the block size?
Quiz¶
Quiz
Today's Class¶
- Architecture
- Memory
- Communication
Goal: AI Tasks¶
- Sentiment Analysis
- Image Recognition
Natural Language Processing¶
- Systems for human language
- Broad area of study with lots of challenges
- Heavily uses ML, more in recent years
Sentiment Classification¶
- Canonical sentence classification problem
- Given sentence predict sentiment class
- Key aspects: word polarity
Image Recognition¶
- Classical problem in intro machine learning.
Data Set¶

Data Labels¶


Problem Setup¶
- Training: Exactly the same as simple
- Loss: Exactly the same as simple
- Models: Mostly similar to the simple problem.
Challenges¶
1) How do we handle input features? 2) How do we look at variable-size areas? 3) How do we predict multiple labels?
Basic NLP¶
Network Challenges¶
- Converting words to tensors
- Converting sentences to tensors
- Handling word combinations
What is a word?¶
- Treat words as index in vocabulary
- Represent as a one-hot vector
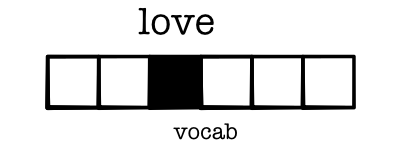
One-Hot Issue¶
- Tens of thousands of words
- Opposite problem as before, 2-features to 10,000
- ``Embedding'' represent high-dim space in low dim
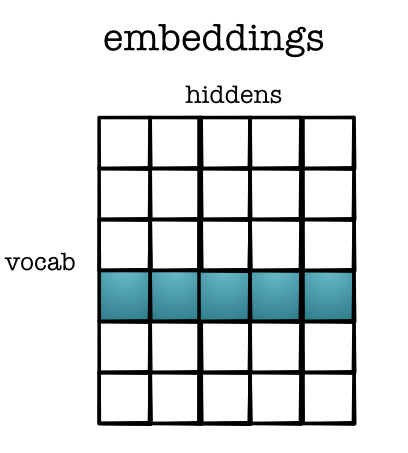
Intuition: Lookup in Table¶
Get word vector
In [3]:
VOCAB = 1000
EMB = 100
embeddings = rand(EMB, VOCAB)
word = 20
embeddings[0, word]
# * Challenge: How to compute `backward`
Out[3]:
0.7649509638874962
Alternative: Lookup by broadcast¶
Get word vector
In [4]:
# word_one_hot = tensor([0 if i != word else 1
# for i in range(VOCAB)])
# embeddings @ word_one_hot.view(VOCAB, 1)
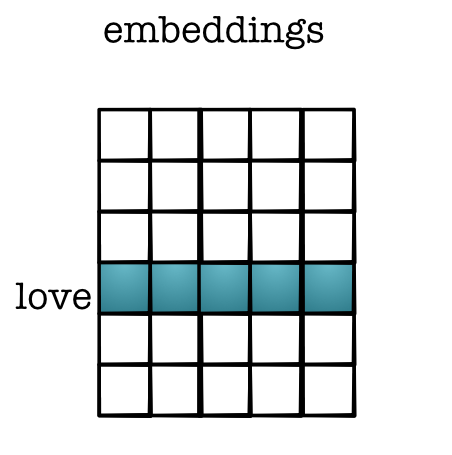
How does this share information?¶
- Similar words have similar embedding dim
- Dot-product - easy way to tell similarity
(word_emb1 * word_emb2).sum()- Differentiable!
Embedding Layer¶
Easy to write as a layer
In [5]:
class Embedding(minitorch.Module):
def __init__(self, vocab_size, emb_size):
super().__init__()
self.weights = \
minitorch.Parameter(minitorch.rand((vocab_size, emb_size)))
self.vocab_size = vocab_size
def forward(input):
return (input @ self.weights.values)
Where do these come from?¶
- Trained from a different model
- Extracted and posted to use
- (Many more details in NLP class)
Examples¶
Query 1
^(lisbon|portugal|america|washington|rome|athens|london|england|greece|italy)$Query 2
^(doctor|patient|lawyer|client|clerk|customer|author|reader)$Challenge 2: Sentence Length¶
- Examples may be of different length
- Need to all be converted to vectors and utilized
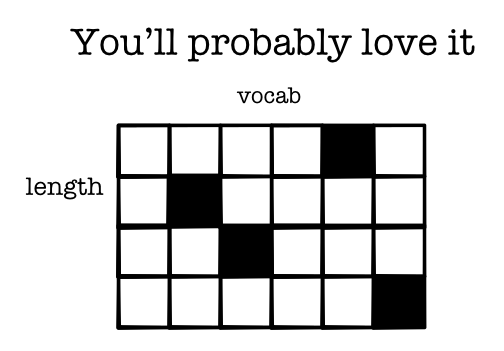
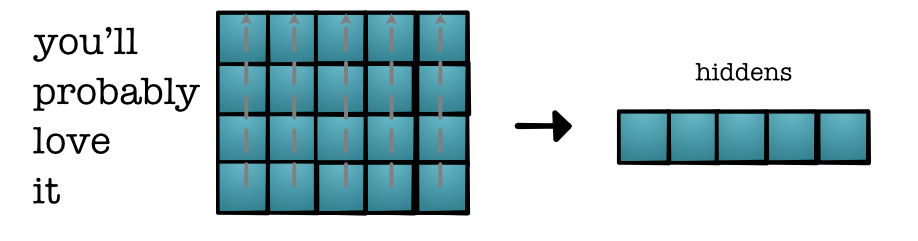
Value Transformation¶
- batch x length x vocab
- batch x length x feature
- batch x feature
- batch x hidden
- batch
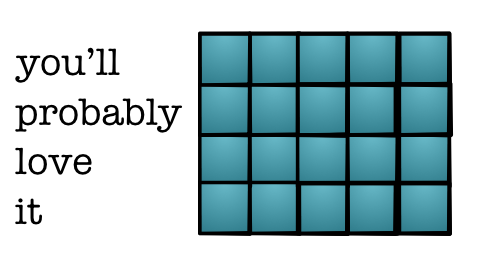
Benefits¶
- Extremely simple
- Embeddings encode key information
- Have all the tools we need
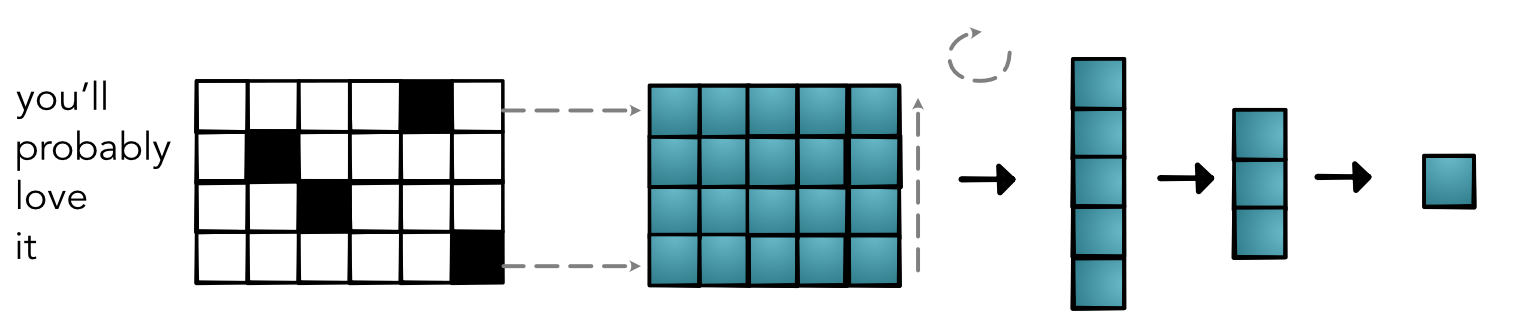
Issues¶
- Completely ignores relative order
- Completley ignores absolute order
- Embeddings for all words, even rare ones
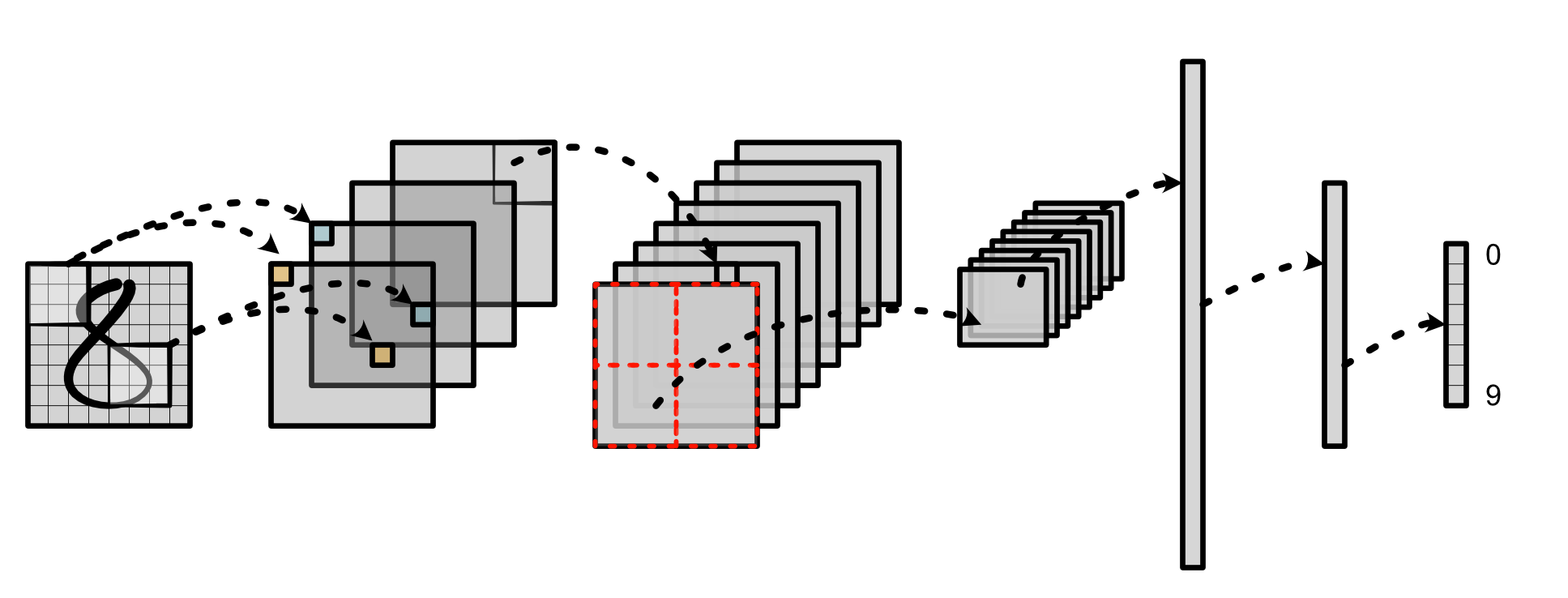
Challenge 1: Input Representation¶

Challenge 1: Input Features¶

Challenge 1: Input Features¶

Challenge 1: Input Representation¶





Challenge 3: Multiple Output¶