Module 4.1 - Convolutions¶
Vector Form¶
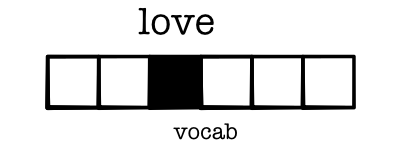
Challenge: Length Dimension¶
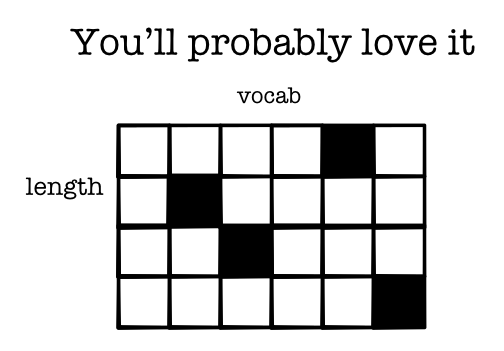
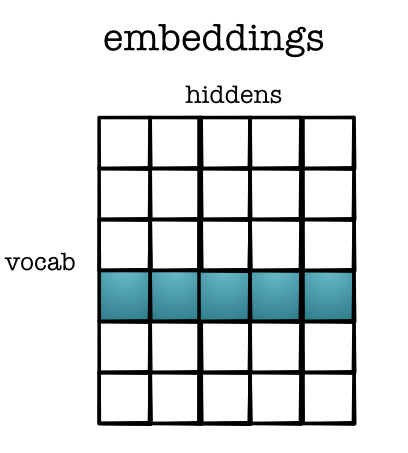
Embedding Table¶
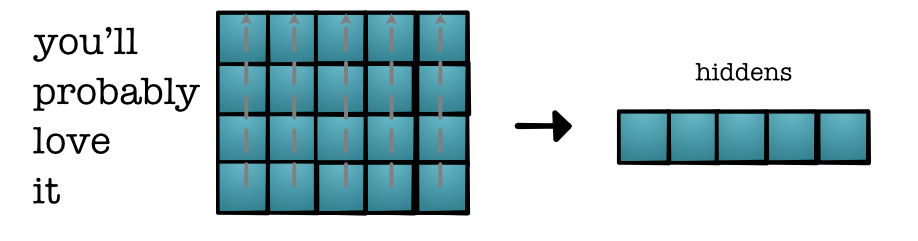
Embedding Layer¶
Easy to write as a layer
In [2]:
class Embedding(minitorch.Module):
def __init__(self, vocab_size, emb_size):
super().__init__()
self.weights = \
minitorch.Parameter(minitorch.rand((vocab_size, emb_size)))
self.vocab_size = vocab_size
def forward(input):
return (input @ self.weights.values)
Reduction / "Pooling"¶
Full Model¶
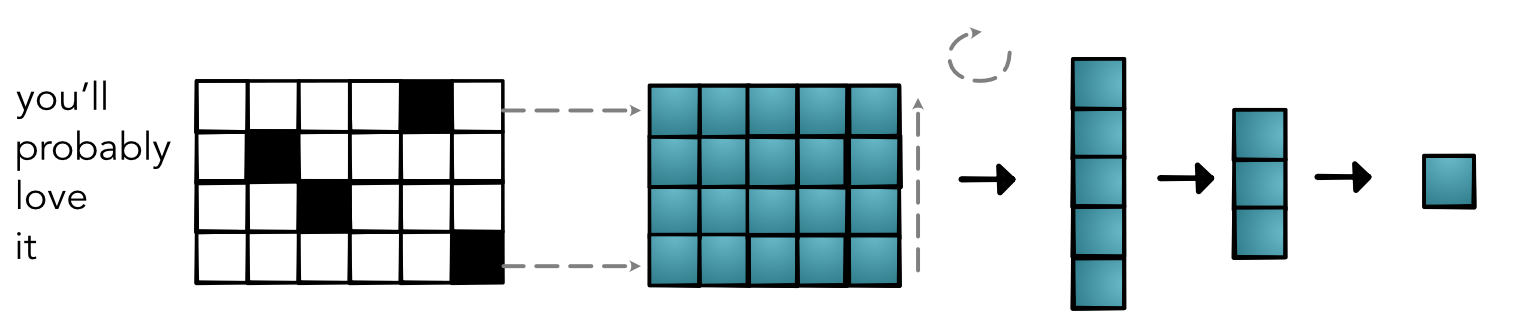
Issues¶
- Completely ignores relative order
- Completley ignores absolute order
- Embeddings for all words, even rare ones
Challenge 1: Input Representation¶

Challenge 1: Input Features¶

Challenge 1: Input Features¶

Challenge 1: Input Representation¶
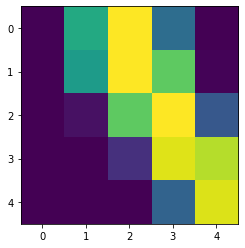
Challenge 2: Variable Size Area¶

Challenge 2: Variable Size Area¶

Challenge 2: MNist Zoom¶

Challenge 3: Multiple Output¶
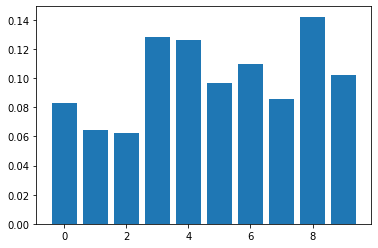
Quiz¶
Quiz
Today's Class¶
- Conv 1D
- Channels
- Conv 2D
Challenge¶
How do we handle locality in features?
NLP¶
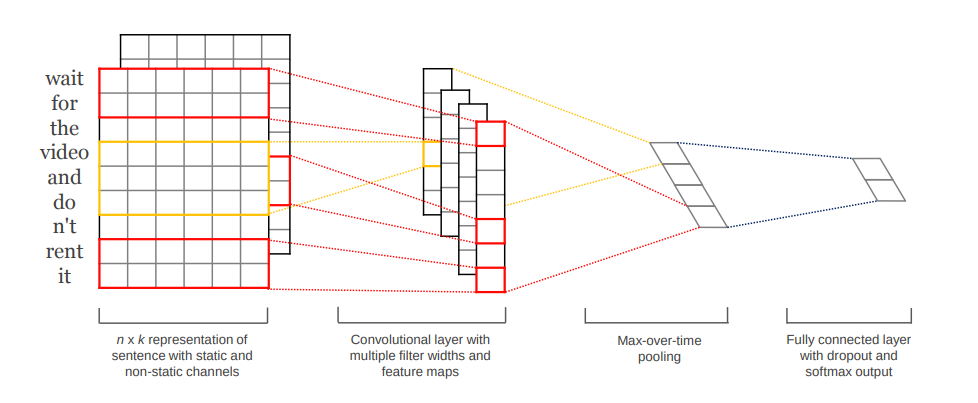
Speech Recognition¶
Intuition¶
- Apply a linear model.
- Run it as a sliding window
- Hope for splits to detect patterns
Convolution Forward¶

Computation¶
Output Values
output[0] = weight[0] * input[0] + weight[1] * input[1] + weight[2] * input[2]
output[1] = weight[0] * input[1] + weight[1] * input[2] + weight[2] * input[3]
output[2] = weight[0] * input[2] + weight[1] * input[3] + weight[2] * input[4]Alternative View¶
Unroll
In [3]:
def unroll(input, T, K):
out = [[input[i + k] if i + k < T else 0
for k in range(K)]
for i in range(T)]
return tensor(out)
Alternative View¶
Unroll
In [4]:
input = tensor([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6])
K = 3
T = input.shape[0]
unrolled_input = unroll(input, T, K)
print(unrolled_input)
[ [1.00 2.00 3.00] [2.00 3.00 4.00] [3.00 4.00 5.00] [4.00 5.00 6.00] [5.00 6.00 0.00] [6.00 0.00 0.00]]
Alternative View¶
Unroll + zip + reduce ::
In [5]:
weight = tensor([5, 2, 3])
output = (unrolled_input @ weight.view(K, 1)).view(T)
print(output)
[18.00 28.00 38.00 48.00 37.00 30.00]
Alternative View¶

Gradient¶
Output Values
output[0] = weight[0] * input[0] + weight[1] * input[1] + weight[2] * input[2]
output[1] = weight[0] * input[1] + weight[1] * input[2] + weight[2] * input[3]
output[2] = weight[0] * input[2] + weight[1] * input[3] + weight[2] * input[4]Gradient¶
In [6]:
class Conv:
@staticmethod
def backward(ctx, d):
...
grad_input[2] = weight[0] * d[2] + weight[1] * d[1] + weight[2] * d[0]
...
Conv Back - Weight¶

Channels¶
Intuition¶
- Each position may have multiple values
- These may be meaningful - i.e. color channels
- These may be learned - i.e. hidden states
Key Points¶
- Convolution is a Linear applied to all channels in position
- If weight is length K and there are 10 channels, the input to the linear is 10 * K.
- Output channels are just like the output of the Linear.
Graphical Representation¶

Code¶
In [7]:
def unroll_chan(input, T, C, K):
out = [[input[i + k, c] if i + k < T else 0
for k in range(K)
for c in range(C)]
for i in range(T)]
return tensor(out)
in_channels = 2
input = rand(T, in_channels)
unrolled_input = unroll_chan(input, T, in_channels, K)
print(unrolled_input.shape) # Shape: T x (in_channels * K)
(6, 6)
Graphical Representation¶

In [8]:
out_channels = 3
weight = rand(in_channels * K, out_channels)
output = unrolled_input @ weight
print(output.shape)
(6, 3)
Implementation¶
- All about understanding sizes.
- Should be similar to matmul, start with output
- If outside boundaries, use 0
Two Dimensional Convolution¶
- Instead of line, now use box
- Box is anchored at the top-left
- Zip-reduce is over full box!
Convolution¶

Conventions¶
Sizes
# Input image - batch x in_channel x height x width
# Weight - out_channel x in_channel x kernel_height x kernel_width
# Output image - batch x out_channel x height x widthBackward¶

Backward¶
Same idea as 1D
- Reverse weight (bottom-top, left-right)
- Anchor bottom-right
- Compute convolution
Implementation¶
- All about understanding sizes.
- Should be similar to matmul, start with output
- If outside boundaries, use 0
Advice¶
- Implement 1D first it is easier
- Compute a couple manually yourself.
- All about indexing


