Module 4.2 - NN and Shapes¶
Convolution Forward¶

Computation¶
Output Values
output[0] = weight[0] * input[0] + weight[1] * input[1] + weight[2] * input[2]
output[1] = weight[0] * input[1] + weight[1] * input[2] + weight[2] * input[3]
output[2] = weight[0] * input[2] + weight[1] * input[3] + weight[2] * input[4]Gradient¶
class Conv:
@staticmethod
def backward(ctx, d):
...
grad_input[2] = weight[0] * d[2] + weight[1] * d[1] + weight[2] * d[0]
...
Graphical Representation¶
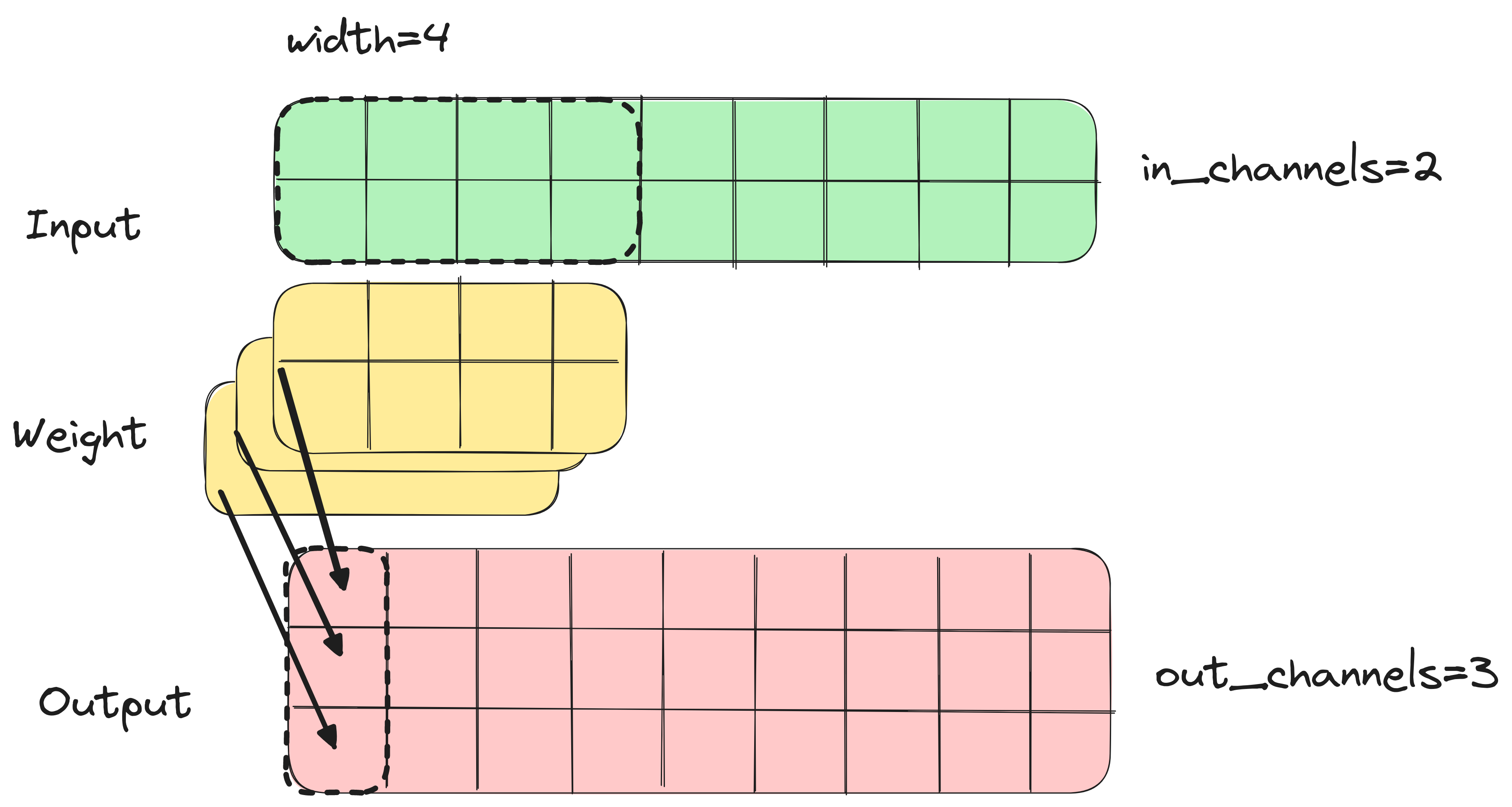
Two Dimensional Convolution¶
- Instead of line, now use box
- Box is anchored at the top-left
- Zip-reduce is over full box!
Convolution¶

Quiz¶
Quiz
Outline¶
- Local Pooling
- ReLU and Sigmoid
- Max and Softmax
Pooling¶
Challenge¶
- How do we look at bigger areas with convolutions?
Pooling¶
- Adjusts the scale at each layer
- Conv stays the same size, image "zooms" out
2D Pooling¶

Goal¶
- Early layers: Capture basic shapes
- Middle layers: How these connect
- Later layers: Full objects
Example¶

Issues¶
- Number of parameters scale with weight size
- Bigger patterns require more ways to split data.
Standard Reduction¶

Why does this work?¶
- View requires contiguous tensor
- View(4, 2) makes strides (2, 1)

Simple Implementation¶
- Reduce along created fold

2D Pooling¶
- Need to isolate squares into a single dimension.
- Tensor origami :)
Exercise¶
- If I have a (10, 10) cube. How do I sum up neighboring rows?
- Goal (5, 10) cube.
ReLU, Step, Sigmoid¶
Basic Operations¶
- Introduced in Module-0
- Widely used in ML
- What is it?
Relationship¶
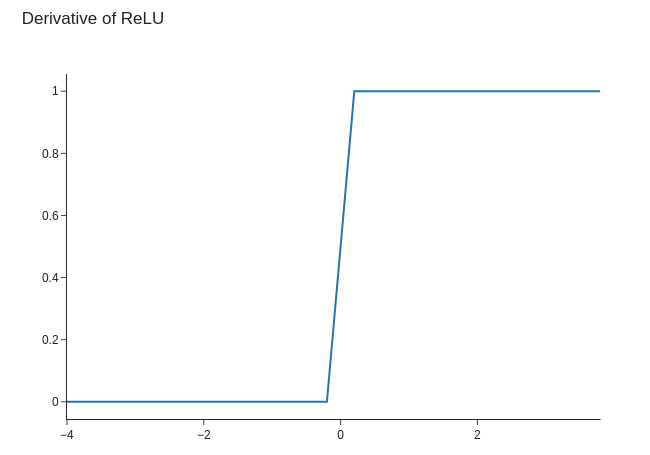
Step is derivative of ReLU
$$ \begin{eqnarray*} \text{ReLU}'(x) &=& \begin{cases} 0 & \text{if } x \leq 0 \\ 1 & \text{ow} \end{cases} \\ \text{step}(x) &=& \text{ReLU}'(x) \end{eqnarray*} $$
Derivative of Step?¶
Mathematically,
$$\text{step}'(x) = \begin{cases} 0 & \text{if } x \leq 0 \\ 0 & \text{ow} \end{cases}$$
Not a useful function to differentiate
Sigmoid acts as a "soft" version¶
Soft (arg)max?¶
Would be nice to have a version that with a useful derivative
$$\text{sigmoid}(x) = \text{softmax} \{0, x\}$$
Useful soft version of argmax.
Max, Argmax, Softmax¶
Max reduction¶
Max is a binary associative operator
$\max(a, b)$ returns max value
Generalized $\text{ReLU}(a) = \max(a, 0)$
Max Pooling¶
- Common to apply pooling with max
- Sets pooled value to "most active" in block
- Forward code is easy to implement
Max Backward¶
- Unlike sum, max throws away other values
- Only top value gets used
- Backward needs to know this.
Max Backward¶
- First compute
argmax - Only send gradient to
argmaxgradinput - Everything else is 0
Ties¶
- What if there are two or more argmax's?
- Max is non-differentiable, like
ReLU(0). - Short answer: Ignore, pick one
Soft argmax?¶
- Need a soft version of argmax.
- Generalizes sigmoid for our new loss function
- Standard name -> softmax
Softmax¶
$$\text{softmax}(\textbf{x}) = \frac{\exp \textbf{x}}{\sum_i \exp x_i}$$
Sigmoid is Softmax¶
$$\text{softmax}([0, x])[1] = \frac{\exp x}{\exp x + \exp 0} = \sigma(x)$$
Softmax¶

Review¶
- ReLU -> Max
- Step -> Argmax
- Sigmoid -> Softmax
Softmax¶
Softmax Layer¶
- Produces a probability distribution over outputs (Sum to 1)
- Derivative similar to sigmoid
- Lots of interesting practical properties
Softmax in Context¶
- Not a map!
- Gradient spreads out from one point to all.